Strategic assets' plan will add fuel to peninsula fire
 |
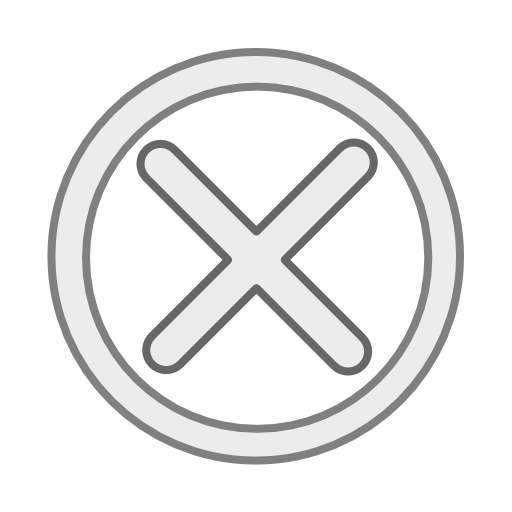
| Democratic People's Republic of Korea launches a long range rocket launched into the air in this file still image taken from KRT video footage, released by Yonhap on February 7, 2016. [Photo/Agencies] |
Pyongyang insisted it was exercising its legitimate right to "self-defense" by firing a ballistic missile over Japan on Tuesday. For the United States, the Republic of Korea, and Japan in particular, it was an exceedingly provocative gesture not seen in almost a decade. So much so that Japan activated its J-Alert system in northern areas, conducted drills to test its anti-ballistic missile system PAC-3; ROK President Moon Jae-in personally ordered live fire drills to exhibit his country's "overwhelming" fire power, with an officer counter-threatening the DPRK leadership with "extermination"; and US President Donald Trump repeated his previous warning that "all options are on the table".
Despite the widespread condemnations, from the United Nations, Japan, the ROK, the US, China, Russia and other countries, the DPRK appears defiant as ever, threatening to fire more missiles into the Pacific.
The story has been unfolding exactly the same way as on each past occasion, and the outcome seems set to be the same: Pyongyang and its critics continuing wrangling over the chicken or the egg causality dilemma, with the former refusing to give up its nuclear pursuit and the latter remaining hopelessly divided over what to do.
If Pyongyang's latest provocation has exposed the helplessness of the international coalition against its nuclear and missile programs, the worse may be yet to come.
One fundamental reason for the international community's inability to curb the DPRK's dangerous adventure has been the contradictory agendas of those that ostensibly have shared interest in denuclearizing the Korean Peninsula. If the Terminal High Altitude Area Defense anti-missile system is the first wedge driving the fragile coalition apart, another, more damaging one seems on its way as Seoul and Washington reportedly engage in talks on deploying additional "strategic assets" on the ROK's soil. Seoul has already confirmed corresponding talks between ROK and US militaries.
Pyongyang's continuous provocations may serve as a catalyst for the potential deployment of additional but controversial and divisive "strategic assets". But like THAAD, US strategic weapons can do little to prevent the feared civilian losses when a war with the DPRK breaks out. However, they can seriously undermine the precious, though already weak, global consensus on the denuclearization of the peninsula, as combined with THAAD, they will constitute a potential, substantial threat to Chinese and Russian national security, and inevitably invite strong reactions from both.
When that day comes, Pyongyang's nuclear/missile programs may turn out to be of secondary concern to the world.