China's National Defense in the New Era

IV. Reform in China's National Defense and Armed Forces
The history of the people's armed forces is a history of reform and innovation. In the new era, China is advancing defense and military modernization across the board and deepening reform in national defense and armed forces in all respects, with a focus on removing institutional barriers and solving structural and policy-related problems to adapt to the trends of worldwide RMA and the demands of national security. Historic strides have been made in strengthening the armed forces.
Reforming the Leadership and Command System
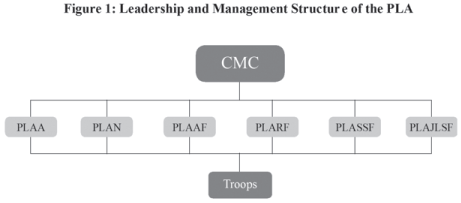
The reform in the leadership and command system is a significant measure in response to the call of a modern and specialized military capable of fighting and winning wars in the information age, aiming to improve the operational effectiveness and development efficiency of the military. Adhering to the general principle of "the CMC exercising overall leadership, the TCs responsible for military operations and the services focusing on developing capabilities", the PLA endeavors to enhance the CMC's centralized and unified leadership and its functions of strategic command and strategic management. The PLA has dismantled the long-established systems of general departments, military area commands (MAC) and the force composition with a dominating land force, and established new leadership, management and operational command systems.
Reorganizing and establishing new CMC functional organs. To optimize the functional and institutional setup of the CMC organs, the former General Staff Headquarters, General Political Department, General Logistics Department and General Armaments Department have been reshuffled into 15 organs under the centralized CMC leadership to advise, execute and serve. Thus, the chains of command, development, management and supervision are more streamlined, and the responsibilities of decision-making, planning, execution and assessment are more properly delegated.
Improving the leadership and management system for services and arms. The PLA has:
? Established the PLAA leading organs by integrating the functions of the former general departments concerning the development of the land force;
? Established the PLASSF by combining strategic support forces across the services and CMC organs;
? Renamed the Second Artillery Force the PLARF; and
? Established the PLAJLSF by integrating strategic and campaign level forces mainly for general-purpose support.
Thus, a CMC-Services-Troops leadership and management system has been put in place.
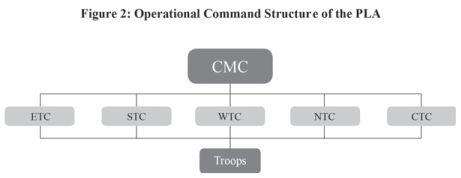
Establishing and improving the joint operations command system. By improving the joint operations command organ of the CMC and setting up those at the theater level, the PLA has established a lean and efficient joint operations command system composed of permanent and specialized commanding establishments for both peacetime and wartime operations. The former Shenyang, Beijing, Lanzhou, Jinan, Nanjing, Guangzhou and Chengdu MACs have been reorganized into 5 TCs: Eastern Theater Command (ETC), Southern Theater Command (STC), Western Theater Command (WTC), Northern Theater Command (NTC), and Central Theater Command (CTC). Thus, a CMC-TCs-Troops operations command system has been established.
Building and improving the law-based supervision system. The Chinese military has established the CMC Discipline Inspection Commission (CMCDIC, also the CMC Supervision Commission, CMCSC) under the direct leadership of the CMC, and dispatched disciplinary inspection teams to the CMC functional organs and all TCs. It has set up the CMC Politics and Law Commission (CMCPLC) and established regional military courts and procuratorates. It has put into place the CMC Audit Office (CMCAO), reformed the audit-based oversight system, and implemented PLA-wide resident auditing. Thus, power is exercised in a way that decision-making, execution and supervision check each other and function in coordination.
Optimizing Size, Structure and Force Composition
Reform in size, structure and force composition is a pivotal step to optimizing military organizational structure and establishing a modern military force structure with Chinese characteristics. Following the instruction to optimize structures, develop new-type forces, adjust proportions and reduce sizes, the PLA is striving to transform from a quantity-and-scale model to that of quality and efficiency, as well as from being personnel-intensive to one that is S&T-intensive.
Adjusting scale and proportion, and restructuring force composition. 300,000 personnel have been cut to keep the total active force at 2 million. Reform measures have been taken to transfer more officer positions to noncommissioned officers and civilian staff, downsize the leading organs at all levels by reducing their subordinate sections, leadership hierarchies and staff, and streamline the institutions and personnel in arts, sports, press, publication, logistical support, medical facilities, depots, and educational and research institutes. Thus, the number of personnel in the leading organs at and above regiment level has been cut by about 25%, and that of non-combat units by almost 50%. The PLA has significantly downsized the active force of the PLAA, maintained that of the PLAAF at a steady number, moderately increased that of the PLAN and PLARF, and optimized the force structures of all services and arms. The PLA has restructured the defense reserves. The deployment of combat forces has been adjusted for a strategic configuration that meets the demands of safeguarding China's national security in the new era.
Reorganizing the troops and rebuilding new-type combat forces. The previous 18 group armies have been reorganized into 13 new ones. All major combat units of the PLA follow a group army-brigade-battalion system. Reform measures have been taken to reinforce the combat capacity of the arms, reduce the command hierarchies and combine the troops at lower levels. New types of combat forces have been enhanced to conduct special operations, all-dimensional offense and defense, amphibious operations, far seas protection and strategic projection, aiming to make the force composition complete, combined, multi-functional and flexible.
Rebalancing and reorganizing military educational and research institutions. The PLA and the PAP have restructured the previous 77 universities and colleges into 44. The National Defense University (NDU) and the National University of Defense Technology (NUDT) have been reorganized. China's armed forces have established the CMC Steering Committee on Military Scientific Research and reorganized the Academy of Military Sciences (AMS) and the research institutes of the services. Thus, the military scientific research forces have been rebalanced with the AMS as the lead, the research institutes of the services and arms as the main forces, and the research components in educational institutions and the troops as supplements.
Reforming Military Policies and Institutions
China's armed forces take combat effectiveness as the criterion in the reform of military policies and institutions and encourage the initiative, enthusiasm and creativity of all members of the armed forces. Reform is designed to build and improve the system of socialist military policies and institutions with Chinese characteristics.
They have deepened reform in the institutions for Party building in the military to uphold the authority of the CPCCC and its centralized and unified leadership, and ensure the absolute leadership of the CPC over the military. Rules and regulations including the Decision of China's Armed Forces on Strengthening Party Building in the Military in the New Era have been formulated to improve the Party's institutions in the military in order to enhance its political and theoretical buildup, consolidate organizations, improve conduct, and enforce discipline.
They have innovated in policies and institutions for military force employment in a bid to effectively perform all missions and tasks in the new era. Rules and regulations have been formulated including the Regulations on Vessel Protection Operations (Trial). The institutions of military strategic guidance, regulations on combat readiness duties, and rules and regulations on joint operations have all been optimized.
They have reformulated policies and institutions to further develop combat capabilities. Laws and regulations have been formulated and amended including the Law of the People's Republic of China on National Defense Transportation, the Law of the People's Republic of China on the Protection of Military Installations and the Regulations on Civilian Personnel in the Military. Newly-updated military training regulations and outlines have been promulgated. They have made progress in establishing the career officers system, optimizing the institutions of military welfare and support, improving the military honors system, and refining policies and institutions in training, equipment development, logistics, military research and national defense mobilization. Meanwhile, bigger legislative steps have been taken in relation to military officers and military service.
They have reformed the policies and institutions for military management to elevate the efficacy of military systems and boost quality development of the military. Rules and regulations have been formulated including the newly-updated Regulations on Routine Service of the People's Liberation Army (Trial), the Regulations on Discipline of the People's Liberation Army (Trial), the Regulations on Formation of the People's Liberation Army (Trial), and the Regulations on Military Legislation. China's armed forces are enhancing institutional innovation in strategic management, defense expenditure management, and the military judicial system.
They have suspended all paid services. As of June, 2018, paid services provided by leading organs, operational units, and military-affiliated public institutions at all levels had been basically suspended, involving 15 sectors such as real estate lease, agricultural and associated products, and hospitality. Over 100,000 such projects have been suspended as scheduled, accounting for 94% of the total. The armed forces have achieved the goal of withdrawing from running businesses.

Reshuffled PLA and PAP Troops
The PLAA plays an irreplaceable role in maintaining China's national sovereignty, security and development interests. It comprises maneuver operation, border and coastal defense, and garrison forces. Under the PLAA, there are 5 TC army commands, the Xinjiang military command, and the Tibet military command. The ETC Army has under it the 71st, 72nd, and 73rd group armies; the STC Army has the 74th and 75th group armies; the WTC Army has the 76th and 77th group armies; the NTC Army has the 78th, 79th and 80th group armies; and the CTC Army has the 81st, 82nd and 83rd group armies. In line with the strategic requirements of maneuver operations as well as multi-dimensional offense and defense, the PLAA is speeding up the transition of its tasks from regional defense to trans-theater operations, and improving the capabilities for precise, multi-dimensional, trans-theater, multi-functional and sustained operations, so as to build a new type of strong and modernized land force.
The PLAN has a very important standing in the overall configuration of China's national security and development. It comprises submarine, surface ship, aviation, marine, and coastal defense forces. Under the PLAN, there are the ETC Navy (Donghai Fleet), the STC Navy (Nanhai Fleet), the NTC Navy (Beihai Fleet), and the PLAN Marine Corps. Under the TC navies there are naval bases, submarine flotillas, surface ship flotillas and aviation brigades. In line with the strategic requirements of near seas defense and far seas protection, the PLAN is speeding up the transition of its tasks from defense on the near seas to protection missions on the far seas, and improving its capabilities for strategic deterrence and counterattack, maritime maneuver operations, maritime joint operations, comprehensive defense, and integrated support, so as to build a strong and modernized naval force.
The PLAAF plays a crucial role in overall national security and military strategy. It comprises aviation, airborne, ground-to-air missile, radar, ECM, and communications forces. Under the PLAAF, there are 5 TC air force commands and one airborne corps. Under the TC air forces, there are air bases, aviation brigades (divisions), ground-to-air missile brigades (divisions) and radar brigades. In line with the strategic requirements of integrating air and space capabilities as well as coordinating offensive and defensive operations, the PLAAF is accelerating the transition of its tasks from territorial air defense to both offensive and defensive operations, and improving its capabilities for strategic early warning, air strikes, air and missile defense, information countermeasures, airborne operations, strategic projection, and integrated support, so as to build a strong and modernized air force.
The PLARF plays a critical role in maintaining China's national sovereignty and security. It comprises nuclear missile, conventional missile and support forces, and subordinate missile bases. In line with the strategic requirements of having both nuclear and conventional capabilities and deterring wars in all battlespaces, the PLARF is enhancing its credible and reliable capabilities of nuclear deterrence and counterattack, strengthening intermediate and long-range precision strike forces, and enhancing strategic counter-balance capability, so as to build a strong and modernized rocket force.
The PLASSF is a new type of combat force for safeguarding national security and an important driver for the growth of new combat capabilities. It comprises supporting forces for battlefield environment, information, communications, information security, and new technology testing. In line with the strategic requirements of integrating existing systems and aligning civil and military endeavors, the PLASSF is seeking to achieve big development strides in key areas and accelerate the integrated development of new-type combat forces, so as to build a strong and modernized strategic support force.
The PLAJLSF, as the main force for joint logistics as well as strategic and campaign level support, is an important component of the modern military force with Chinese characteristics. It comprises the support forces for inventory and warehousing, medical services, transport, force projection, oil pipelines, engineering and construction management, reserve assets management, and procurement. Under the PLAJLSF, there are 5 joint logistic support centers located respectively in Wuxi (Jiangsu Province), Guilin (Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region), Xining (Qinghai Province), Shenyang (Liaoning Province), and Zhengzhou (Henan Province), as well as the PLA General Hospital and the PLA Center for Disease Prevention and Control. In line with the requirements of joint support for joint operations and joint training, the PLAJLSF is being integrated into the joint operations system to enhance the capabilities of integrated joint logistics, so as to build a strong and modernized joint logistic support force.

The PAP shoulders important responsibilities in safeguarding national security, social stability and public wellbeing. China has adopted a CMCPAP-Troops leadership and command system with the basic duties and nature of the PAP unchanged. The PAP is not in the force structure of the PLA. The PAP border defense, firefighting and security guard forces have been decommissioned. The coast guard under the leadership of State Oceanic Administration has been transferred to the PAP. PAP goldmine, forest and hydroelectricity forces have been reorganized into specialized forces of non-active service under corresponding state authorities. Meanwhile, the PAP customs guard forces have been withdrawn. In this way, the leadership, management, command and employment of the PAP has become more coherent. Following adjustment and reorganization, the PAP is mainly composed of the internal security corps, the mobile corps, and the coast guard. In line with the strategic requirements of performing multiple functions and effectively maintaining social stability, the PAP is enhancing capacity in guard duties, emergency response, counter-terrorism, maritime rights protection, administrative enforcement and disaster relief, so as to build a strong and modernized armed police force.
Promoting Defense and Military Development in All Respects
Placing theoretical and political buildup at the top of the agenda of the armed forces. China's armed forces unswervingly take Xi Jinping's thinking on strengthening the military as the guidance, firmly uphold General Secretary Xi Jinping as the core of the CPCCC and the whole Party, firmly uphold the authority of the CPCCC and its centralized and unified leadership, and follow the CMC Chairman responsibility system, in an effort to further strengthen the consciousness of the need to maintain political integrity, think in big-picture terms, follow the leadership core and keep in alignment. In accordance with the Decision on Issues Relating to the Military Political Work in the New Era issued in December 2014, China's armed forces have improved their political work and embarked on a new journey of development. In order to fully strengthen the Party leadership and Party building of the military in the new era, a CMC meeting on party building was held in August, 2018. Great efforts are being made to cultivate revolutionary officers and soldiers of the new era with faith, ability, courage and integrity, and build troops with iron-like faith, conviction, discipline and commitment.
Promoting innovation in defense S&T and military theory. China's armed forces are accelerating the implementation of the strategy to develop the military through S&T in a bid to maintain and enhance the strength of the areas where they lead, and intensify innovation in emerging areas. They have made great progress in independent innovation in some strategic, cutting-edge and disruptive technologies, and succeeded in developing strategic hi-tech products such as the Tianhe-2 supercomputer. Focusing on war and fighting wars, China's armed forces have innovated in military doctrines and delivered outcomes in military strategy, joint operations and informationization, which have provided a theoretical support to defense and military development.
Establishing a modernized weaponry and equipment system. China's armed forces are optimizing the overall composition of weaponry and equipment, coordinating the efforts of all services and arms in this regard, promoting the balanced development of main battle equipment, information systems, and support equipment, with a view to comprehensively raising standardization, serial development and interoperability. Old equipment is being phased out, and a system created that mainly comprises new and high-tech weaponry and equipment. Type 15 tanks, type 052D destroyers, J-20 fighters, and DF-26 intermediate and long-range ballistic missiles have been commissioned.
Building a combat-oriented modern logistics system. China's armed forces are putting in place a support mechanism combining centralized and decentralized support, as well as general and special-purpose supplies, with PLAJLSF as the backbone force and service logistics units as supplements. They are also building a joint, lean and efficient logistic support system with the strategic and campaign level forces as the main force, the affiliated forces as the support, and the civil sectors as supplements. Logistics units have been incorporated into TC-level joint training, trans-theater training by services and arms, and joint exercises and training with foreign militaries to strengthen the integrated training of logistical and operational forces. China's armed forces have acquired a rapid, multi-dimensional and precise support capability.
Strengthening strategic management. Adopting demand-oriented planning and planning-led resource allocation, China's armed forces have established and improved the strategic management procedures of demand-planning-budgeting-execution-evaluation. They have completed a system of strategic plans and programs composed of the development strategies of the military as a whole, and its key areas, branches, and the PAP. They have regulated military strategic planning, promulgated and implemented the Outline of the 13th Five-Year Plan for Military Development, and optimized the mechanisms for evaluation, supervision and control.
Governing the military with strict discipline and in accordance with the law. China's armed forces are building a military legal system with Chinese characteristics and pressing ahead with a fundamental transformation in how the military is run. They are strengthening oversight and supervision in military training and combat readiness to uproot peacetime ills. They are promoting legal awareness through public communication and education campaigns, establishing and improving the support mechanism of legal consultation and service, and advancing law-based management in the military. China's armed forces are striving to manage the troops more strictly in all respects. They have fully implemented military rules and regulations, restored and improved the traditional mechanism of using bugles to communicate and command, carried out safety inspections to identify and tackle potential problems, stepped up garrison military policing, strengthened the management of military vehicles by targeted measures, and set up a mechanism of regular notification on garrison military policing. These efforts have contributed to maintaining the positive image of the armed forces.
Improving Party conduct, upholding integrity and continuing the fight against corruption. China's armed forces are tightening political discipline and rules, investigating and dealing strictly with grave violations of CPC discipline and state laws as in the cases of Guo Boxiong, Xu Caihou, Fang Fenghui, and Zhang Yang. China's armed forces punish corruption in strict accordance with CPC discipline and relevant laws, and rectify any malpractice in key construction projects and the procurement of equipment and material. Points-of-contact for discipline supervision have been designated at the small-unit level to investigate and combat "micro corruption" and misconduct in all its forms among service members. China's armed forces have intensified political inspection by completing disciplinary inspections and re-inspections over all CMC functional organs, the TCs, services, AMS, NDU, NUDT and the PAP. They have worked to implement full-spectrum audit, intensify the audit of major fields, projects and funds, and perform strict audits over the economic liabilities of officers in positions of leadership. Active efforts have been made to monitor the cost-effectiveness of applied funds, conduct whole-process audit, and combine civil and military efforts in auditing. Since 2012, they have carried out audits over 39,000 units and 13,000 PLA and PAP officers in positions of leadership at and above regiment level. As a result, notable achievements have been made in the fight against corruption in China's armed forces, and a healthy political atmosphere of integrity has formed.
Modernizing national defense mobilization. China has refined the system of national defense mobilization to enhance the development of its defense reserves. China is streamlining the number of primary militia nationwide, driving deeper reform of militia and reserve forces in their size, structure and composition, promoting integrated development and employment of the reserve and active forces, and extending the function of national defense mobilization from mainly supporting the land force to supporting all branches at a faster pace.
In the process of deepening the reform of the CPC and governmental institutions, the Ministry of Veterans Affairs of the PRC has been set up. Through a series of preferential measures, the veteran support system is progressing at provincial, prefectural, county, town and township (sub-district), and village (community) levels. Substantial steps have been taken to enhance the government's efforts to support the military and their families, and to strengthen the military's support to the government and the people. China's armed forces play an active role in poverty alleviation. The relationships between the military and the government and between the military and the people are getting even closer. There is a growing consensus across communities to respect and give preferential treatment to all service members.