Saving the past to secure the future


Shortly after Zhu Yuanzhang, the founding emperor of the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644), expanded the territory to present-day Anshun, Guizhou province, he thought of a way to consolidate his governance over the newly gained land.
Tens of thousands of his loyal followers in today's Anhui province as well as other regions in East China, mostly soldiers and their families, migrated long distances to get stationed in the fortified villages, known as tunpu. They retained the customs and traditions of their hometown, which are distinctive from surrounding indigenous communities, including dialects, food, clothing, and, of course, music.
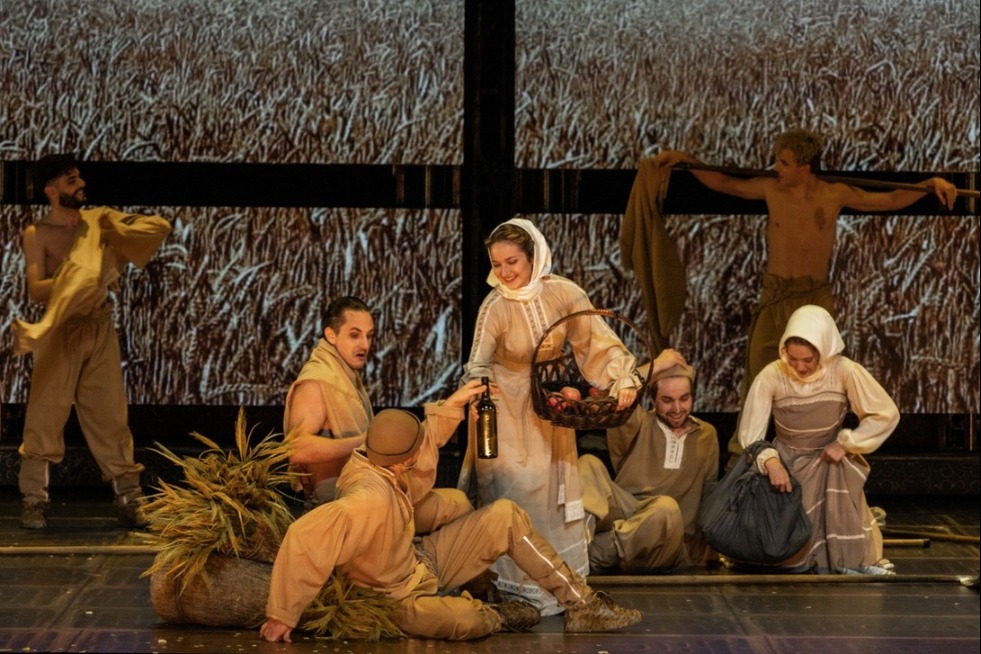
For people living in tunpu, a folk opera form known as dixi ("the opera on the ground") has been a key ingredient for their rituals. Telling ancient wartime legends, from the depths of history, the opera genre has become a pillar art form to pass down patriotism and loyalty from one generation to another.
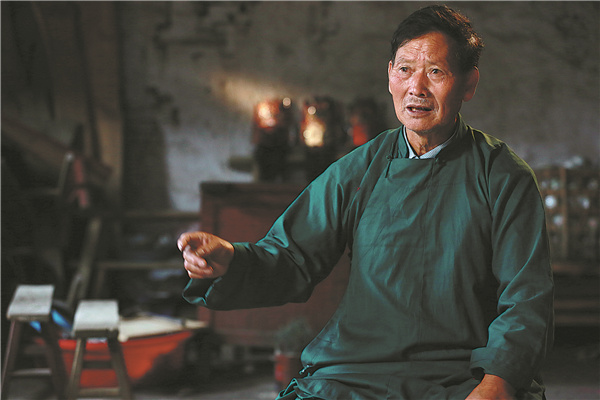
For Zhan Xueyan, a senior dixi performer, that opera has been part of his memory since childhood.
"As long as my father wore performance clothes, I'd like to follow," he says. "Just like my youngest grandson did when I prepared to perform."