The sound of global connections
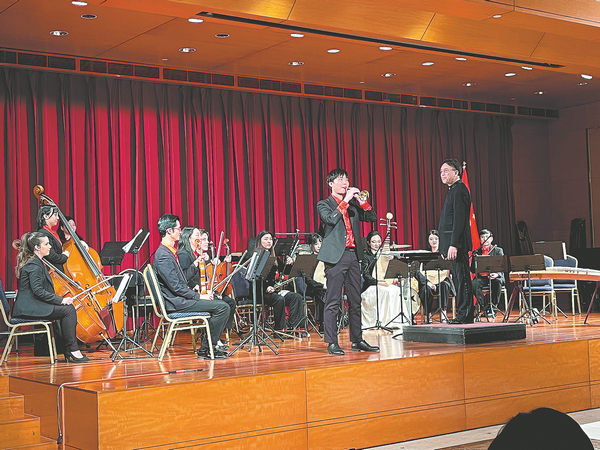


Liu and her partner are planning to compose music after graduation that is based on a fusion of Chinese elements with other styles.
"We focus on contemporary Chinese music, incorporating its elements with jazz, particularly emulating the jazz style that emerged in Shanghai when jazz first arrived in China. We also explore modern interpretations of Chinese pop music," says Liu. She says one highlight of her work is the emphasis on improvisation.
"Traditional Chinese music has many opportunities to be performed in the United States, but when people think of Chinese music, they often only think of the pentatonic scale," says Liu. A pentatonic scale has five notes per octave, in contrast to the heptatonic scale, which is common in Western music.
"Chinese music is much more diverse than many realize, with a variety of new elements. We aim to introduce these to American audiences and believe blending Chinese music with other styles is important. We would love to use our creative work to explore the future of Chinese music," she says.
Across different historical periods, European countries adapted classical music from Central Europe and Austria, spreading it to Norway, Finland and Russia, where it evolved into their own styles, says Cai, recalling the history of classical music. He believes the 21st century marks a new phase where Asia, especially China, is transforming symphonic music into its own art form.
"If you visit concert halls in the United States, you'll see that the audience is mostly elderly. New works rarely receive significant performances. I think this is a global issue, especially in the West. I believe we haven't reflected on how our music should represent contemporary voices," Cai says.
By establishing the Chinese music program at Bard College in New York, Cai hopes to explore Chinese music with contemporary voices.
Contact the writer at minluzhang@chinadailyusa.com