North China Plain

The North China Plain is among China's three major plains and serves as a vital cradle of early civilization. Its significance became increasingly apparent with the development of agricultural civilization. Throughout history, various states and dynasties recognized the strategic importance of this region and constructed segments of the Great Wall across the North China Plain to fend off invasions by nomadic tribes from the north. Notably, the states of Zhao during the Warring States Period (475-221 BC), the Qin Dynasty (221-206 BC), the Han Dynasty (206 BC-AD 220), the Northern Qi Dynasty (550-577), as well as the Ming Dynasty (1271-1368), all contributed to the construction and reinforcement of the Great Wall in this area. These efforts reflect the ongoing need to protect the fertile and densely populated plains, which were crucial for sustaining the agricultural and economic stability of the region.

The Great Wall constructed during the Northern Qi Dynasty (550-577): The Northern Qi Dynasty undertook the construction of two significant lines of the Great Wall to bolster their defenses against various threats. To deter raids by nomadic tribes such as the Tujue (Turkic peoples) and the Khitan, they built a segment of the Great Wall known as the "Outer Wall." This wall stretched from what is now the northwest of Shanxi to the Shanhaiguan Pass in Hebei, forming a crucial defensive barrier against northern incursions. In addition to the Outer Wall, the Northern Qi Dynasty also faced threats from the west, specifically from the Northern Zhou Dynasty (557-581). To fortify against this western threat, they constructed another section of the Great Wall, referred to as the "Inner Wall". This wall extended from present-day Pianguan in Shanxi to Changping in Beijing.


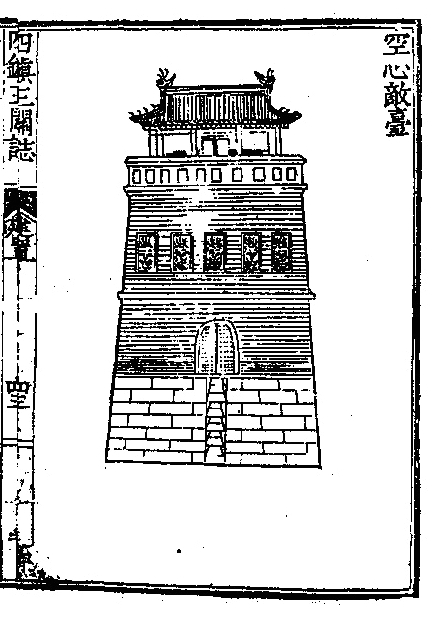
Jizhen Town Great Wall of the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644): The Jizhen Town section of the Ming Dynasty's Great Wall winds along the Yan Mountains, traversing steep terrain where slopes often exceed 50 degrees. A distinctive hallmark of this stretch is the profusion of hollow watchtowers. These towers, erected atop the Great Wall, boast windows on all four sides and functioned as garrison posts. Soldiers stationed inside could also store their weapons and ammunition inside the towers. This innovative design effectively mitigated the challenges of soldiers being exposed to harsh weather conditions without shelter and the logistical difficulty of storing military supplies on the wall during battles.

During the mid to late Ming Dynasty, Jizhen Town gradually expanded to include Zhenbao Town, Changping Town and Shanhai Town. These expansions further strengthened Jizhen Town's defense system, making it an even more crucial part of the Ming Dynasty's military defenses. Zhenbao Town was renowned for its famous defensive structures such as Zijing Pass and Daomaguan, while Changping Town included strategic locations like Badaling and Juyong Pass, which were key components of the Great Wall's defensive network at that time.