Loess Plateau sees remarkable ecological transformation
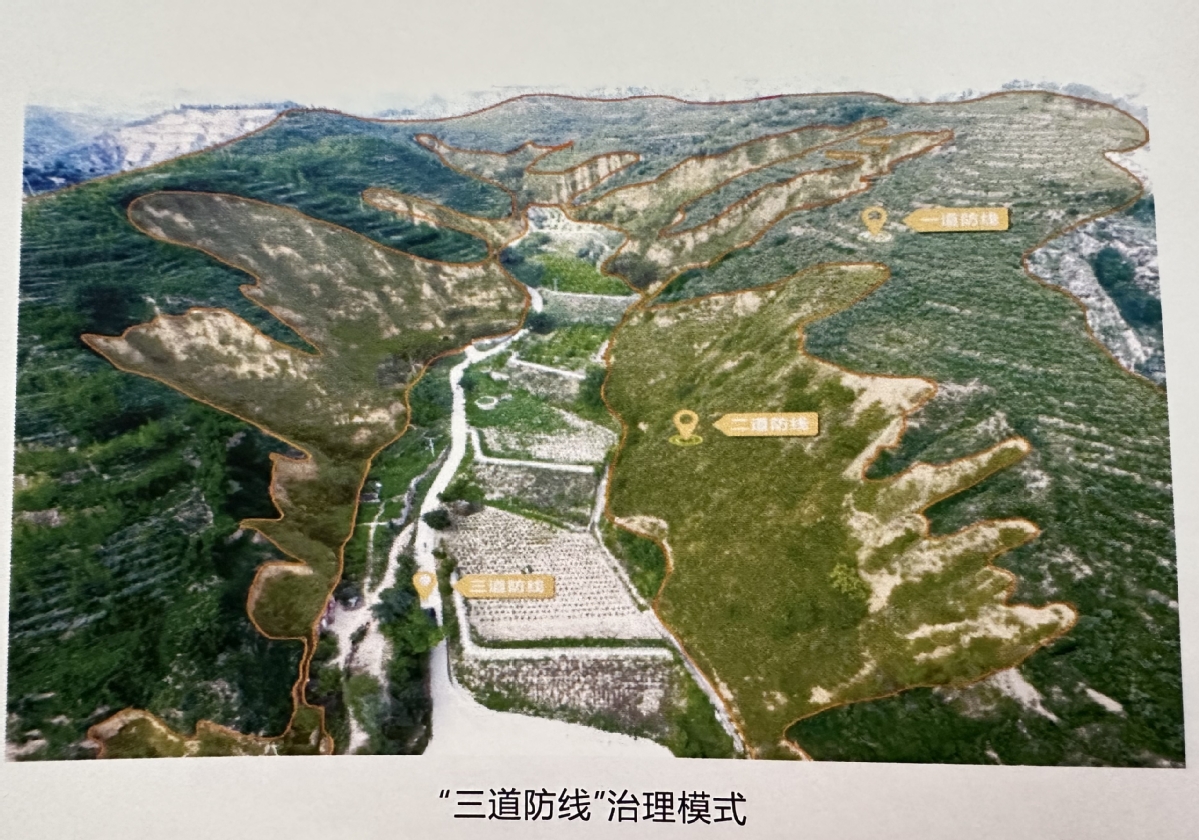


The system, spanning from hilltops to ravine bottoms, acts as a multi-layered defense against soil erosion. When rainfall occurs, the vegetation on slopes acts as "security guards," preventing sediment runoff.
The sediment trapped by warp land dams is utilized for planting various cash crops. Xindiangou also conducted research on soil and water conservation forests and economic forests, introducing a variety of fruit trees and other species for experimental plantations.
Supported by this model, Xindiangou currently boasts over 100 species of woody plants, more than 30 types of grasses, with a vegetation coverage exceeding 75 percent, achieving an impressive sediment trapping rate of 98 percent.
This system has significantly raised the soil conservation rate to 80 percent, with the lush greenery becoming invaluable assets, according to Gao.
The success of this model has led to its widespread promotion and application across provinces including Shaanxi, Shanxi, and the Inner Mongolia autonomous region, yielding substantial results.