Watching the water
 |
|
Photo Provided to China Daily |
He later was given more professional pollution-detection equipment by Hangzhou-based e-commerce giant Alibaba Group, who initiated the Qingyuan Action for water protection in 2011. The project aimed to build a platform for individual participation and to encourage local nongovernmental organizations to assist the provincial government in water protection.
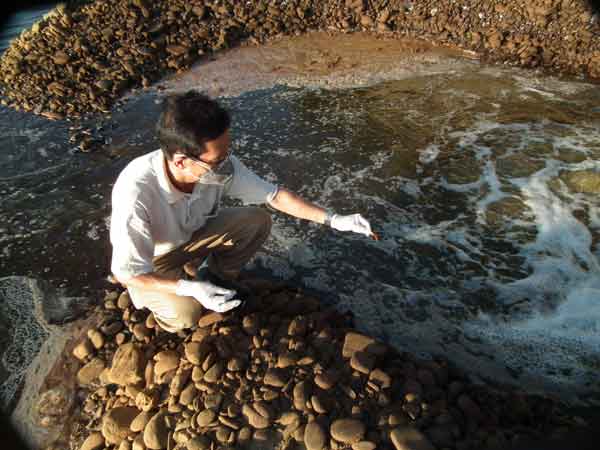
Dong, along with more than 30 volunteers, including lawyers, students, taxi drivers and salesmen, were invited to be river monitors. Twice a week they visit the three main stretches of the Qujiang River, the main source of the Qiantang River that runs through southeast China, investigate pollution sources, take photos, perform basic water quality tests and report problems they find.
| Not talking trash |
Xu Jianfang, a 40-year-old taxi driver in Quzhou, was persuaded by Dong to join the action in 2011. Now he is the backbone of the group.
"Actually Dong did not talk too much but said some simple truths: Water quality is vital to health and to our children. It was the right thing," Xu says, adding that he was also touched by Dong's passion for the cause.
Xu is responsible for monitoring the 40-km-long Wuxi River with about 40 to 50 industrial wastewater outlets. He says factories are now under more pressure thanks to the cooperation between NGO and governmental environment supervisors.
"We would first inform the factory if we found it discharged untreated wastewater. Many of them knew us, and would stop pollution immediately. They knew if they ignored it, we report to the authorities," he says.
About 82 percent of China's rivers and lakes are affected by different levels of pollution, according to Wang Hao, an expert from the China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research.
In the highly industrialized southeastern Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta, it is common for 500 to 600 factories to be crowded along a 100-km-long riverbank, which means the discharged pollutants are far beyond the river's capacity to absorb them, Wang says.
He suggests raising the industrial water drainage standard and increasing the pollution discharge fees might help.
At the grassroots level, Dong, who has been fully devoted to the project, believes it is the attention and action from ordinary people that can change the situation. "As a lawyer I work for the benefit of my clients. Now I work for the good of the majority. This inspires me to carry on," he says.
For more China Face, here